How to Choose the Right Voltage Regulator: A Quick Guide

A voltage regulator is an essential component in any electrical system, ensuring a consistent and stable supply of voltage to your devices. These regulators are designed to prevent voltage fluctuations, which can cause damage to sensitive electronics or lead to system inefficiencies. Whether you’re powering industrial machinery or household appliances, the right voltage regulator ensures safety, longevity, and optimal performance.
Selecting the correct voltage regulator is critical for protecting your equipment and achieving energy efficiency. The wrong choice can result in overheating, poor performance, or even equipment failure. This guide will provide a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to choosing the best voltage regulator for your specific needs.
What Is a Voltage Regulator and Why Is It Important?

Key Roles of a Voltage Regulator
Stabilizing Power Supply: Voltage regulators smooth out fluctuations in voltage, preventing damage to sensitive components.
Protecting Equipment: They shield devices from voltage surges, spikes, or drops that could lead to malfunctions or permanent damage.
Enhancing Efficiency: By maintaining a consistent power supply, voltage regulators optimize the performance and lifespan of your equipment.
Consequences of Using the Wrong Voltage Regulator:
Overheating: An incompatible regulator may overheat and fail prematurely.
Device Malfunction: Incorrect voltage can cause erratic behavior or complete failure of connected devices.
Energy Waste: Inefficient regulation leads to energy loss and higher operational costs.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Voltage Regulator


Types of Voltage Regulators: Which One Suits Your Needs?
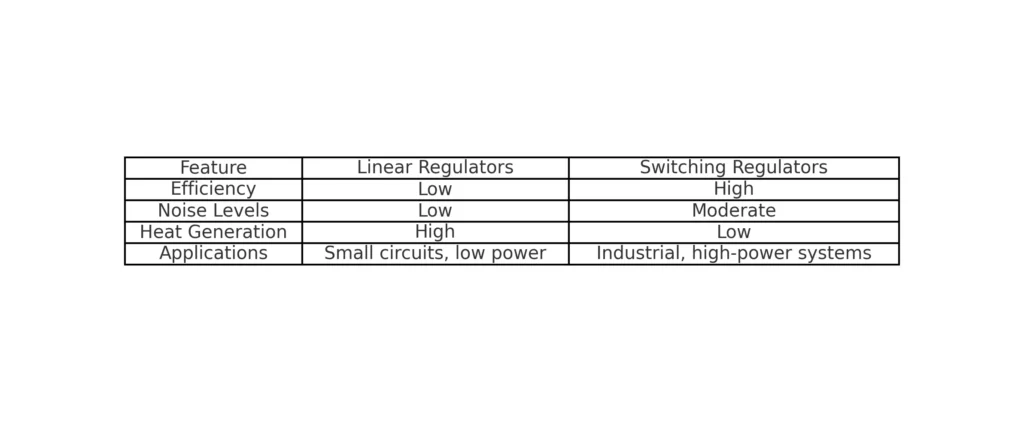
Voltage regulators come in different types, each tailored to specific applications. Linear voltage regulators use resistive components to drop excess voltage, making them simple, low-noise, and cost-effective. However, they are inefficient at high loads due to heat generation, making them best suited for small electronics and audio systems. Switching voltage regulators, on the other hand, employ high-speed switching and energy storage components like inductors, offering high efficiency, compact size, and the ability to handle large loads. They are ideal for industrial machinery, automotive systems, and renewable energy setups, though they generate moderate noise. Specialized voltage regulators, such as programmable and adjustable types, cater to custom voltage requirements in advanced systems like labs. Selecting the right regulator involves understanding your power needs, budget, and the specific requirements of your application to ensure efficiency and reliability.
Comparison Table:
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting a Voltage Regulator
Even with a solid understanding of voltage regulators, mistakes can happen. Avoid these common pitfalls:
Choosing Based on Cost Alone: Cheap regulators may lack the durability or performance needed for your system. Tip: Balance cost with quality and specifications.

Ignoring Power Capacity
An underpowered regulator may fail to support the load, leading to overheating and inefficiency.
Tip: Always check the load capacity and ensure it exceeds your system’s requirements.
Overlooking Environmental Factors
Regulators not designed for harsh conditions may degrade quickly.
Tip: Choose ruggedized models for extreme environments.
Neglecting Maintenance Needs
Regulators require periodic checks to ensure optimal performance.
Tip: Opt for models with simple maintenance requirements.
Avoiding these mistakes can save you time, money, and potential system failures.
Steps to Choose the Right Voltage Regulator
- Identify Your Power Source: Measure the input voltage range and fluctuations.
- Determine Load Requirements: Understand the voltage and current needs of your devices.
- Evaluate Efficiency: Choose a regulator that balances performance with energy savings.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the regulator fits your system’s physical and electrical specifications.
- Test Before Use: Conduct a trial run to verify performance.

Top Voltage Regulator Recommendations for Different Applications
Top Voltage Regulator Recommendations for Different Applications
FAQ
Selecting the right voltage regulator is crucial for maintaining the performance, safety, and longevity of your electrical systems. By understanding your specific needs and avoiding common mistakes, you can ensure reliable power regulation. For expert advice or tailored solutions, don’t hesitate to consult a professional. A stable power supply is the foundation of efficient operations—invest in it wisely!